Herniated lumbar disc
What is a herniated disc lumbar disc?
The spine is made up of a number of individual bones called vertebrae. These are stacked to form the spinal column. Between every joint in the spine is a cushion called intervertebral discs, these act as shock absorbers. Each of these discs has a gel-like centre, which is called the nucleus pulposus, that is surrounded fibrous outer layer called the annulus.
A herniated disc is also referred to as a ruptured or slipped disc and occurs when pressure from above and below vertebrae force some of the nucleus pulposus through a torn part of the annulus. Technically any of the disc material can cause a herniation (migration of disc material away from where it typically sits).
The lower part of the spine (lumbar spine) is where a herniated disc is most likely to occur, however, they can also occur in the thoracic and cervical spine. Pain in the back and leg are the most likely to be the result of a lumbar herniated disc.
What are the symptoms of a lumbar herniated disc?
Symptoms of a herniated disc in the low back can include:
- Low back pain
- Muscle weakness
- Pain in the buttocks, feet and legs
- Feet or legs experiencing tingling or numbness
What causes a lumbar herniated disc?
A herniated lumbar (low back) disc is caused when the outer layer of the disc becomes weak, resulting in tearing. There are a number of factors that can contribute to this, including age, excessive weight, and strains caused by lifting something heavy or improper twisting.
How common are lumbar herniated discs?
Herniated discs are very common, especially in men. People aged 35-55 years are most likely to experience a lumbar herniated disc.
How is a lumbar herniated disc diagnosed?
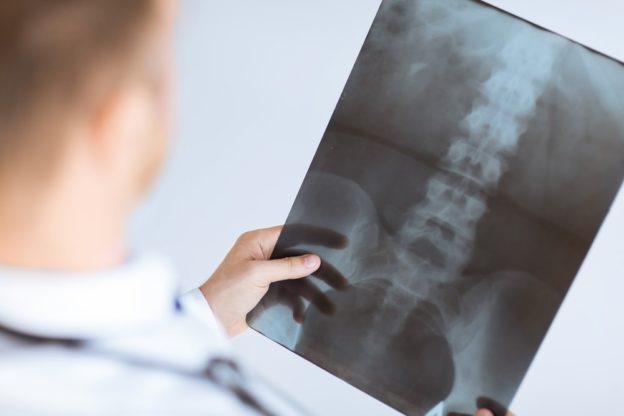
Diagnosis includes an evaluation of your history, symptoms and physical examination by an experienced chiropractor. They may also perform a neurological exam that tests your muscle strength, sensation and reflexes. Other forms of diagnostic tests may also be performed to determine the severity of the herniated disc, these could include:
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) scan and Computer Tomography (CT): An MRI and CT scan develop images of intervertebral discs
How is a lumbar herniated disc treated?
In some cases, a herniated disc can heal on its own, though when treatment is required it involves anti-inflammatory medication, chiropractic and physical therapy. If there is no improvement through these methods of conservative treatment, then surgery or spinal injections may be required. The details of these treatment methods are listed below.
- Chiropractic: Chiropractic is recommended for any low back pain as a first port of call. Chiropractors are trained in the diagnosis and treatment of low back pain and offer a vast resource to improve low back pain from a lumbar disc herniation.
- Medicine: Medications may be recommended by your doctor to help alleviate pain
- Spinal injections: This involves an injection into the lower back, that contain a cortisone-like medication. The goal of this injection is to alleviate inflammation and swelling
- Surgery: While surgery is rare it may be required if a patient is showing little to no response from conservative treatments or has advancing symptoms
Visit us at Sydney Spine & Sports Centre for more information.