At Elemental Chiropractic we offer a holistic approach blended with conventional chiropractic techniques that leaves you feeling connected, uplifted and positive for the future.
Our Mission
Our Purpose

Our Vision
About Us
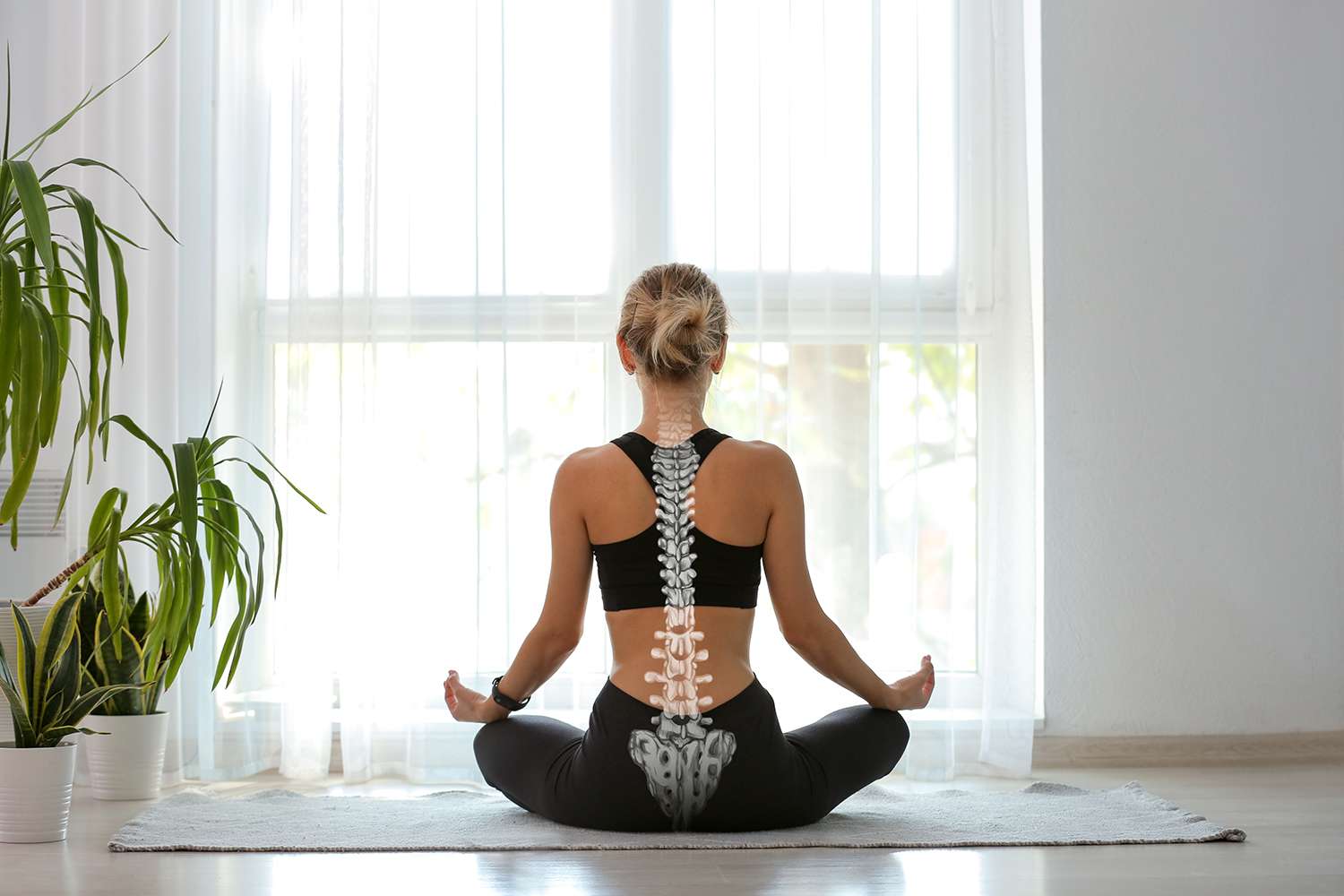
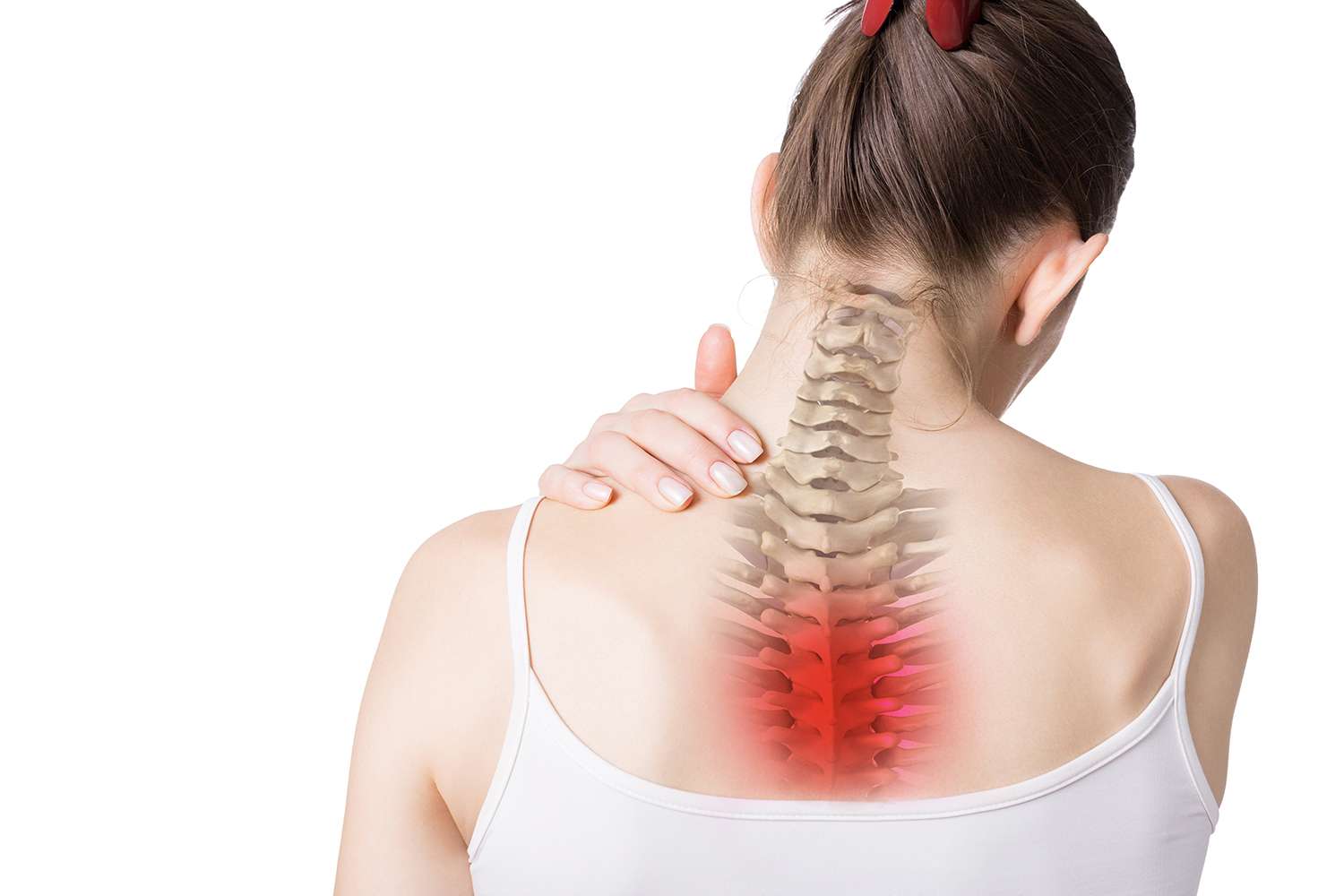
Elemental Chiropractic offer chiropractic services to patients throughout the Inner West suburbs of Balmain & Rozelle, Sydney. Our Balmain chiropractors diagnose, treat, prevent and manage disorders of the neuromusculoskeletal system.
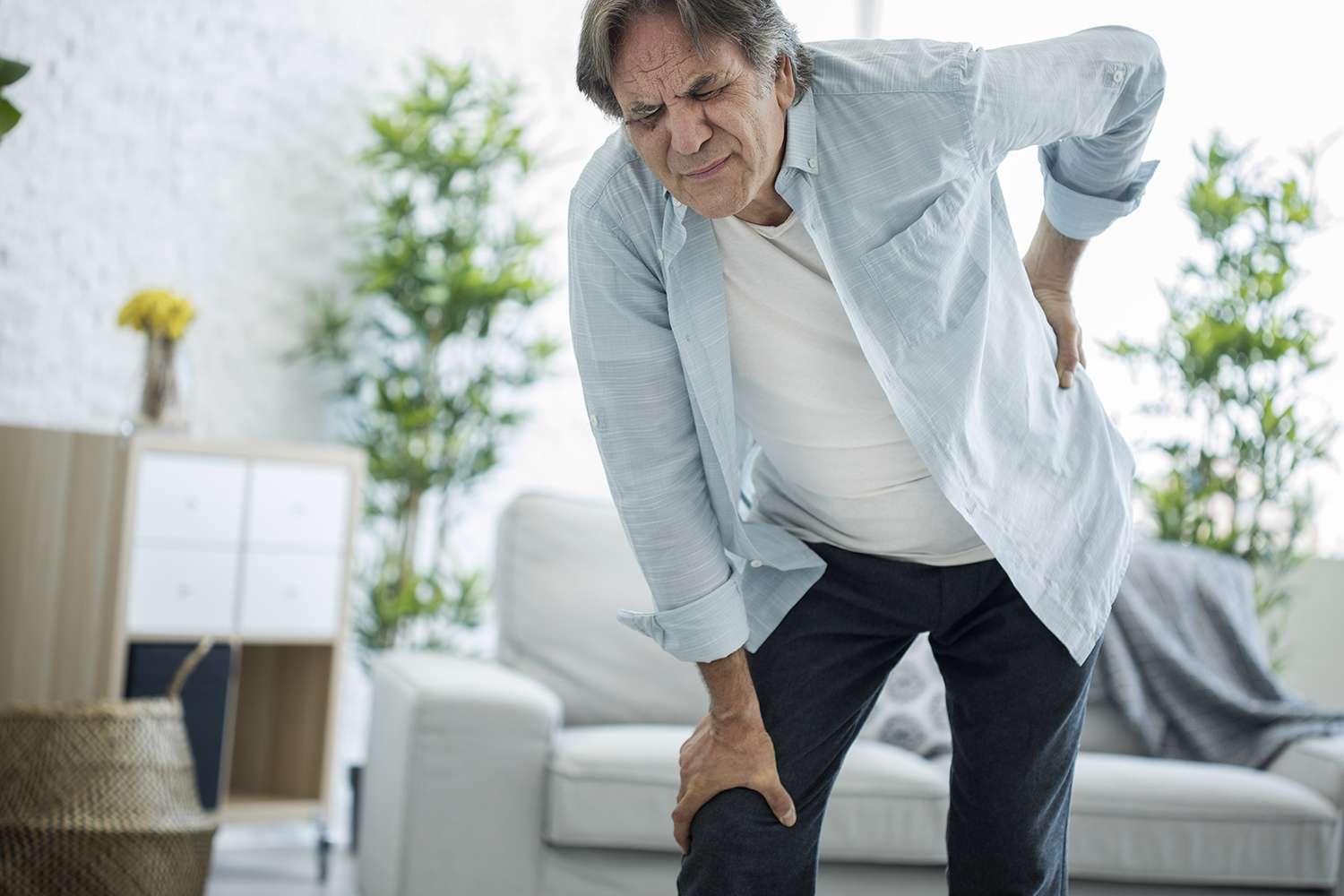
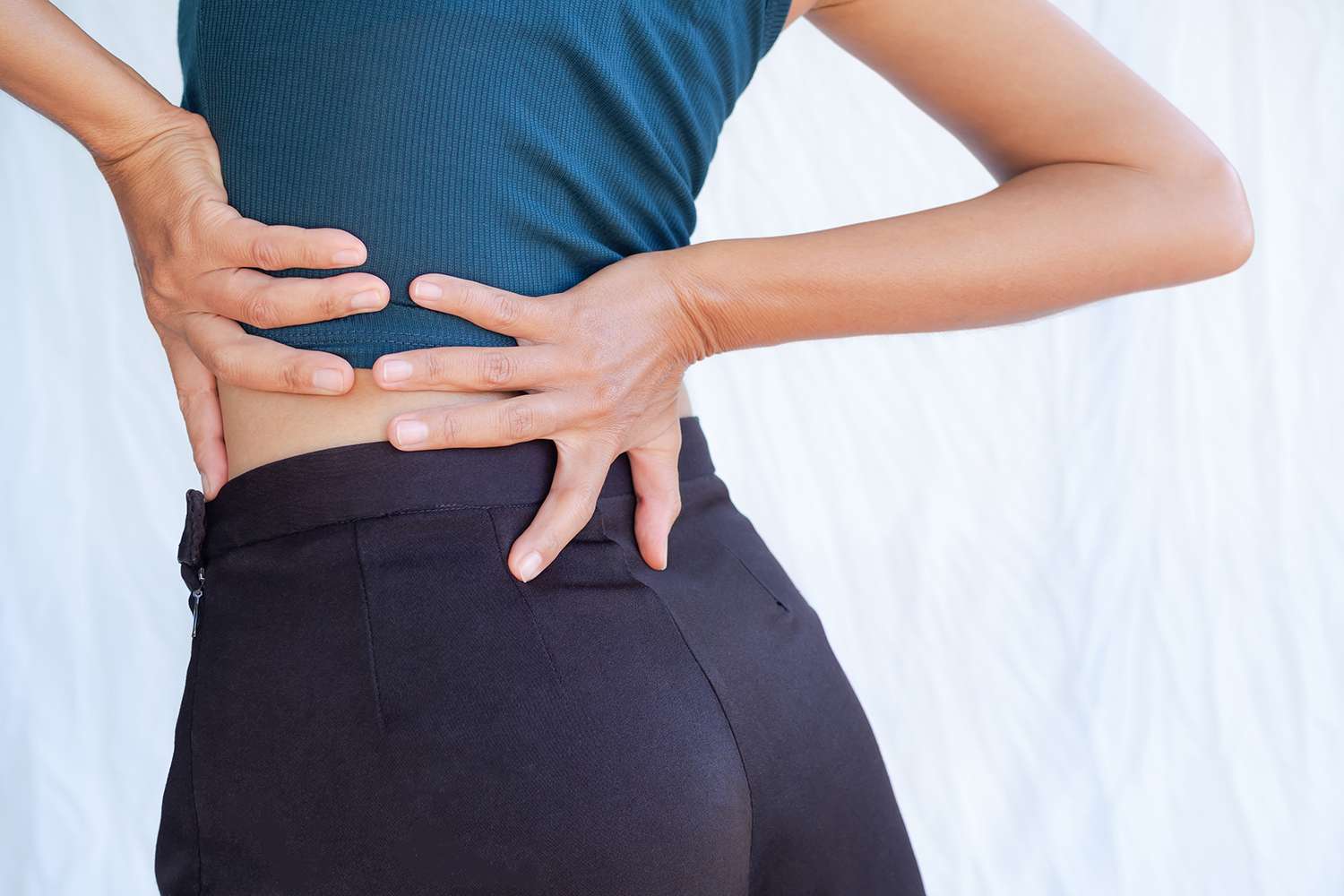
Our chiropractors treat spine, sports, muscle and joint injuries including back pain, neck pain, sciatica, pinched nerves, slipped discs and sports and spine injuries, problems and conditions.
Genuine Care. Honest Advice. High Quality Treatments.
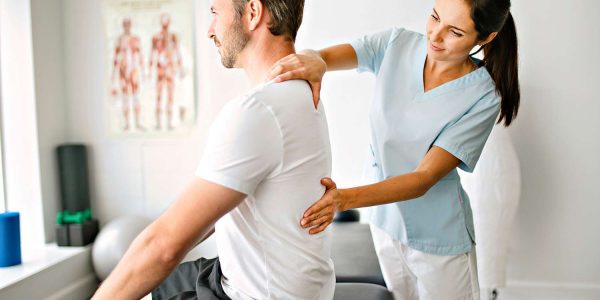
Our philosophy and practice rests on a model of comprehensive and effective care. To treat our patients with the highest quality of care, our chiropractors use the most effective evidence-based techniques and methods.
Every patient is respected as an individual, which encompasses their own unique history. This carries forward how we tailor our chiropractic approach for the best results. We take the time to get to understand the patient including their personal goals as well as their short and long health goals. We then honestly tell them if we can assist in helping to achieve these goals!
Elemental Guides and Articles
Book An Appointment
Elemental is a chiropractic clinic located in Balmain in the innerwest of Sydney. We offer an evidence-based chiropractic treatment approach for spinal, extremity, cranial and somatovisceral imbalances. Our chiropractor performs the necessary history, examination, diagnosis, evaluation and treatments during your appointments, which are conducted in a friendly, relaxed environment.
At Elemental we help guide your body to begin the healing process. We also offer additional ways to improve your overall function and wellness. This can often include take home recommendations for exercises, healthy habits and preventative measures.
Visit our Balmain clinic for safe, effective and ethical treatments delivered by a chiropractor who is passionate about your overall health and well-being.
Associations